LLMs.txt for AI Search Report 2026
LLMs.txt for AI Search Report 2026
LLMs.txt for AI Search Report 2026
A comprehensive study of the necessity of LLMs.txt pages for AI search visibility

Niclas Aunin
Niclas Aunin
Niclas Aunin
Jan 23, 2026
Jan 23, 2026
Jan 23, 2026


Do You Need an LLMs.txt to be visible in AI Search in 2026?
Many blogs and social media posts recommend implementing LLMs.txt as a critical step to improve visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT. It would have been easy for me to jump on the hype and sell an LLMs.txt generator or something similar. However, before doing so, I wanted to validate whether it’s actually beneficial.
To evaluate the effectiveness, I conducted a simple study around two central questions:
Does having an LLMs.txt give me an advantage in AI Search?
Assumption: If LLMs.txt provides a measurable advantage, we should see pages with an /llms.txt outperform their peers in AI visibility.
To validate this, I reviewed three different rankings of high performing domains and checked how many of the websites publish an LLMs.txt:
The top 50 of Ahrefs Most cited domains in AI mode
The top 50 of GPT Insights most emotionally powerful German brands in ChatGPT
Using the top 20 domains based on our own AI Search Report: News & Media
The latter two were included to reduce bias and gain different perspectives. Global, high authority domains may benefit from factors beyond LLMs.txt (brand strength, legacy authority, and large SEO budgets). Narrowing the lens to local rankings and a specific industry dataset helps create a more balanced view of this complex topic.
Do AI models use LLMs.txt when retrieving information?
Assumption: If LLMs.txt were a preferred retrieval format, we would see pages with an /llms.txt show up frequently in cited sources used for grounding.
To test this, I pulled a proprietary AI search dataset containing 94,000+ cited URLs from 11,000+ AI responses monitored by ALLMO.ai between August and December 2025. The dataset includes responses from five leading models: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and Perplexity. Responses with no URL citations were removed beforehand. To ensure broad coverage, the prompt set spans multiple industries and intents (B2B, consumer, enterprise, SMB, etc.) and is large enough in scale to support statistically significant conclusions.
But before we dive into the data, let’s quickly clarify what an LLMs.txt is and what it is not.
What LLMs.txt is, and what it is not?
LLMs.txt is a plain text or Markdown file placed at your site's root directory (yourdomain.com/llms.txt) that curates your most important pages and information for AI consumption. Proposed by Answer.AI in September 2024, it's designed to provide large language models with a clean, prioritized map of your content, think of it as a "context guide" rather than an access control mechanism.
Although LLMs.txt is inspired by robots.txt, which was designed for search crawlers and other automated bots, LLMs.txt is not a permission file and not an indexing directive. It does not control what AI systems are allowed to access. Instead, it acts as an AI specific suggestion file, a voluntary signal that highlights which content you consider important for large language models to prioritize when they interact with your site.
The critical distinction is that LLMs.txt remains non-standard. No formal standards body governs its syntax or semantics, and multiple variants exist (per-page Markdown files, llms-full.txt, script embeds). This fragmentation limits consistent parser behavior across AI platforms.
The data: LLMs.txt adoption across dominant players in AI search
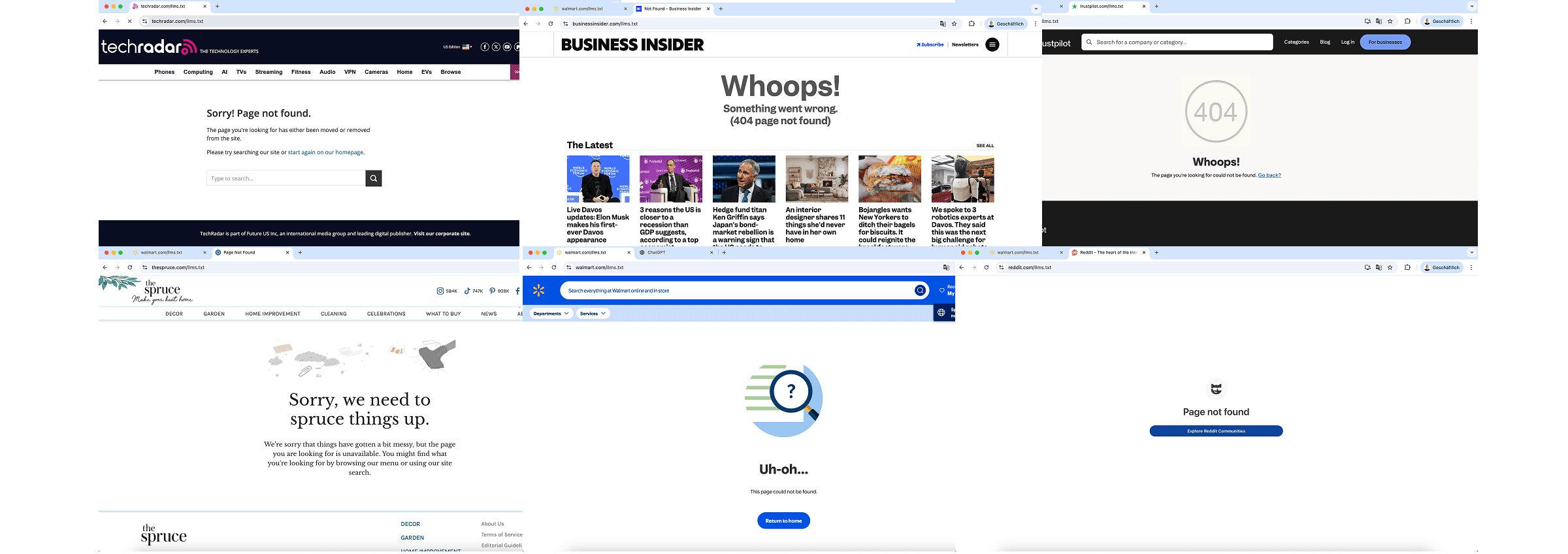
Finding: The data shows only 1 out of the 50 most cited domains in AI search has an /llms.txt file. Target.com was the only company with the file available at target.com/llms.txt.
Remarkably Walmart, already had an /llms.txt page publicly available in November 2025, but a follow-up check in January 2026 it in had been removed.
The implication from the first data set is clear: To make it to the top, you don't need an LLMs.txt. fact, there is no indication that it provides a measurable advantage at all, based on the reviewed dataset (see below).
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|
1 | Not found | |
2 | Not found | |
3 | Not found | |
4 | Not found | |
5 | Not found | |
6 | Not found | |
7 | Not found | |
8 | Not found | |
9 | Not found | |
10 | Not found | |
11 | Not found | |
12 | Not found | |
13 | Not found | |
14 | Not found | |
15 | Not found | |
16 | Not found | |
17 | Not found | |
18 | Not found | |
19 | Not found | |
20 | Not found | |
21 | Not found | |
22 | Not found | |
23 | Not found | |
24 | Not found | |
25 | Not found | |
26 | available | |
27 | Not found | |
28 | Not found | |
29 | the‑sun.com | Not found |
30 | Not found | |
31 | Not found | |
32 | Not found | |
33 | Not found | |
34 | Not found | |
35 | Not found | |
36 | Not found | |
37 | Not found | |
38 | merriam‑webster.com | Not found |
39 | Not found | |
40 | Not found | |
41 | Not found | |
42 | Not found | |
43 | Not found | |
44 | Not found | |
45 | Not found | |
46 | Not found | |
47 | Not found | |
48 | Not found | |
49 | Not found | |
50 | Not found |
Next, I reviewed a dataset of the most emotionally resonant German brands in AI Search (GPTInsights). Compared to the Ahrefs dataset above, this ranking differs in three important ways:
Germany-only scope: The dataset focuses exclusively on German companies. While the Ahrefs list suggests you do not need LLMs.txt to be globally dominant, it is still possible that the file could benefit local or niche players.
Mentions, not citations: The dataset tracks mentions rather than grounded citations. This matters because even if LLMs.txt is not used for grounding, it could theoretically influence whether a company is mentioned more frequently.
Resonance-based ranking: The ranking is based on emotional resonance and sentiment, not just citations. In other words, it measures not only whether brands appear in responses, but whether models reflect positive sentiment toward them.
Finding: The results strongly reinforce the Ahrefs conclusion. None of the Top 50 German brands publish an LLMs.txt file.
You can build strong brand positioning that resonates in ChatGPT without LLMs.txt. Again, there is no evidence that such pages provides a measurable advantage for AI Search visibility.
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Marke | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Feuerwehr Deutschland | Not found | |
2 | Ärzte ohne Grenzen | Not found | |
3 | Miniatur Wunderland Hamburg | Not found | |
4 | Landliebe | Not found | |
4 | Milka | Not found | |
6 | dm Drogeriemarkt | Not found | |
6 | Europa‑Park | Not found | |
6 | Ravensburger | Not found | |
6 | Rotes Kreuz (DRK) | Not found | |
6 | Wikipedia (DE) | Not found | |
11 | Haribo | Not found | |
11 | Lidl | Not found | |
11 | Stiftung Warentest | Not found | |
14 | ADAC | Not found | |
14 | Ritter Sport | Not found | |
14 | Schleich | Not found | |
14 | Wacken Open Air | Not found | |
18 | Porsche | Not found | |
18 | WWF Deutschland | Not found | |
20 | Ahoj‑Brause | Not found | |
20 | Bärenmarke | Not found | |
20 | Caritas Deutschland | Not found | |
23 | Duden (Online) | Not found | |
23 | Fressnapf | Not found | |
23 | Glashütte Original | Not found | |
26 | Apotheken Umschau | Not found | |
26 | Not found | ||
26 | Decathlon | Not found | |
26 | Dr. Oetker | Not found | |
26 | Gerolsteiner | Not found | |
26 | NABU | Not found | |
26 | Nutella | Not found | |
26 | Phantasialand | Not found | |
26 | Tagesschau | Not found | |
26 | Vaude | Not found | |
36 | Alnatura | Not found | |
36 | Brot für die Welt | Not found | |
36 | Deuter | Not found | |
36 | Hilton Hotels | Not found | |
36 | Rotkäppchen Sekt | Not found | |
36 | Tempo | Not found | |
36 | Zalando | Not found | |
43 | Amazon | Not found | |
43 | Bosch | Not found | |
43 | Check24 | Not found | |
43 | Coca‑Cola | Not found | |
43 | Ferrero | Not found | |
43 | Faber‑Castell | Not found | |
43 | Fritz‑Kola | Not found | |
43 | Greenpeace Deutschland | Not found |
Last, I analysed data from the ALLMO AI Search Report: News & Media where I regularly share insights on how AI Searches the web. It tracks results across ChatGPT-4, ChatGPT-5 and Perplexity.
This time, we are looking at a dataset from a specific industry. Media companies where reach is critical, and where some players have training data deals with AI Companies.
By zooming in on a specific industry, we can compare apples to apples and test a simple hypothesis: if /llms.txt has a meaningful impact, publishers using it should outperform their peers.
Again, none of the top domains contained an llms.txt, despite being consistently cited as prominent sources over multiple months.
0 out of the Top 20 media and publishing companies have an LLMs.txt
Even platforms like YouTube, which show especially high visibility in Perplexity, do not publish an LLMs.txt.
Notably, even TechCrunch (ranked #1 in the report category “Start-ups & Technology”) has no LLMs.txt. Meanwhile, a little hope for LLMs.txt advocates, TechStartups does implement the standard, ranks #4 in that category, and sits outside the Top 50 overall. In other words: the standard isn’t even widely adopted among tech-forward publishers, and we don’t see an observable performance advantage in this dataset.
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|
1 | Not found | |
2 | Not found | |
3 | Not found | |
4 | Not found | |
5 | Not found | |
6 | Not found | |
7 | Not found | |
8 | Not found | |
9 | Not found | |
10 | Not found | |
11 | Not found | |
12 | Not found | |
13 | Not found | |
14 | Not found | |
15 | Not found | |
16 | Not found | |
17 | Not found | |
18 | Not found | |
19 | Not found | |
20 | Not found | |
21 | Not found | |
22 | Not found |
Lastly, I wanted to evaluate whether llms.txt is a preferred format for AI models when retrieving information via live web search. If the format had a meaningful positive impact, you’d expect many /llms.txt URLs to show up in citations used for grounding, right?
To test this, I downloaded a dataset from the ALLMO.ai database that I had previously used for research and hypothesis testing. It spans a wide range of industries, query types, and research intents, and statistical significance is strengthened by the sheer amount of results as well.
The results were underwhelming.
1 out of 94,614 cited URLs from 11,867 AI responses collected by allmo.ai was an /llms.txt page.
I had hoped to be able to write a longer section with nuanced findings by industry, model differences, or recommendations on which llms.txt structure performs best. But with only 0.00105693% of AI-cited URLs pointing to llms.txt pages, the conclusion stays the same no matter how you slice it.
Across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini, and Grok, there is no indication that models prefer llms.txt pages when performing live web search, regardless of industry, site structure, or llms.txt structure.
More independent evidence
The data paints a sobering picture. Adoption among major brands remains extremely low and is concentrated primarily in developer documentation and technical tooling sites. Despite the proliferation of WordPress plugins and CMS generators that make implementation trivial, fewer than 10% of websites have implemented LLMs.txt according to seranking.com.
But maybe these 10% of companies are the one's that are going through the roof in AI Search? Our data tells a different story.
More critically, major AI and search vendors have not committed to parsing or relying on LLMs.txt. Google Search representatives have publicly stated that their AI systems do not currently use the file. Ahrefs' independent audit found no confirmed visibility uplift attributable to LLMs.txt across major domains.
Consistent with my findings from the ALLMO.ai llms.txt study, SE Ranking's analysis of 300,000 domains reinforced this finding: websites with LLMs.txt showed no statistically significant difference in AI citation frequency compared to those without it.
Limitations
As always, there are limitations to this analysis:
I did not benchmark websites with llms.txt against website without llms.txt
However, if ~10% of websites have adopted LLMs.txt as reported by seranking, you would expect roughly ~10% of cited sources to include it, and even more if it had a positive impact. Instead, I found the file in less than 1% of the 120 analyzed websites. Since the sample spans multiple locations and industries, this effect appears negligible.
I did not evaluate a single websites performance before and after introducing an llms.txt
Everyone is free to test it on their own sites, but such experiments have limited interpretability: AI search algorithms change frequently, making it difficult to isolate the effect of a single change. If there were a consistent preference or measurable uplift, it should have shown up in the citation data. That said, this does not fully rule out edge cases in specific industries or individual setups.
Key Findings: LLMs.txt does not give any quantifiable benefits.
To summarize, here are the results from our extensive analysis of LLMs.txt adoption and citation impact:
1 out of 94,614 cited URLs from 11,867 AI responses collected by ALLMO.ai cited any /llms.txt page.
Only 1 out of 50 most cited domains in AI Search according to Ahrefs use llms.txt
None of the Top 50 strongest emotional German Brands in ChatGPT use llms.txt
None of the Top 20 most cited media and publisher domains use llms.txt.
Neither ChatGPT nor any other analyzed AI model showed a preference for citing LLMs.txt pages, nor did companies with LLMs.txt consistently outrank competitors without it.
Qualitatively, these findings also align with official statements from major AI and search vendors, suggesting there is no hidden preference or roadmap dependency on LLMs.txt today.
This also let's us answer the initial research questions:
Does LLMs.txt give me an advantage in AI Search?
No measurable advantage is visible in current citation patterns.Do AI models use LLMs.txt when searching for information?
We do not see models using it either as a prioritized content map (to cite pages from it), nor as a direct retrieval source during live web search.
So, do you need to add an llms.txt to your website? A decision lens for 2026
The answer depends entirely on what you publish and who consumes it.
You do not need an LLMs.txt if you operate a consumer content site, marketing property, or general publishing platform. There is no proven citation lift for these use cases today, and most visible brands achieve strong AI visibility without it. The data strongly suggests that AI models do not rely on LLMs.txt as a directive mechanism.
That said, there are a few scenarios where publishing an LLMs.txt can still make sense, even though these benefits are not primarily related to AI search visibility.
You should implement LLMs.txt if you run developer documentation, API references, SDKs, or other agent-facing content. These environments can benefit immediately because coding assistants, IDE integrations, MCPs, and RAG pipelines actively seek clean, structured documentation. Providing LLMs.txt and llms-full.txt reduces noise, improves retrieval accuracy, and makes your content easier to ingest programmatically. Cloudflare, Mintlify, and Anthropic publish these files for their developer docs as part of a broader AI-consumability strategy.
The downside of implementing it is minimal when well curated. If your CMS can auto-generate the file, treating it as future proofing can make sense, as long as you do not expect immediate ROI.
Outlook: from one file to per-page AI signals
The LLMs.txt ecosystem may evolve significantly before it matures, or it may fade entirely.
The likely evolution path currently points toward per-page, machine-readable context rather than a single site-level file. Platforms like Context7 are already experimenting with per-page AI metadata that provides granular, document-level signals. This approach mirrors how structured data evolved: from site-wide declarations to page-specific schema markup.
The pragmatic stance for 2026 and beyond: invest in AI-consumable content and reliable agent access now. Treat LLMs.txt as optional scaffolding, not a primary visibility lever. The fundamentals, clear structure, accurate information, machine-friendly formatting, will outlast any single file format.
FAQ: Quick answers about LLMs.txt and AI search visibility
Will LLMs.txt boost my AI citations today?
Unlikely for most sites. Major AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI experiences do not currently appear to rely on LLMs.txt as a primary retrieval or ranking input (based on public statements and independent audits). In addition, ALLMO.ai’s analysis of 94,000+ cited URLs found no measurable citation uplift associated with LLMs.txt adoption.
Is there any harm in adding it?
Usually not, if it’s accurate and maintained. Implementation cost is low, and many CMS platforms offer one click generation.
The risk comes from:
poorly curated files (noise, outdated or incorrect context)
manual effort with low ROI (opportunity cost)
technical SEO mistakes (for example duplicate content or wrong indexing signals if configured incorrectly)
Who benefits most right now from llms.txt?
Developer documentation and API publishers. If your audience uses IDE agents, coding assistants, or RAG pipelines, llms-full.txt and clean Markdown exports can improve machine ingestion because these systems actively seek structured documentation.
My logs shows ChatGPT crawled my llms.txt. So it's useful, right?
Not necessarily. Crawling alone does not imply impact. Bots crawl many pages on most websites, and llms.txt can be treated like any other URL. What matters is whether it shows up in retrieval and citation behaviour, which currently appears rare.
What can I do instead to grow my presence in AI search results
There are many proven ways to improve AI Search visibility beyond LLMs.txt, and the GEO and ALLMO industry is evolving fast, with new tactics and findings emerging constantly. If you want to learn about about ways to optimize your site, talk to me or explore more ways to optimize in The ALLMO Blog.
Key Takeaways
LLMs.txt appears in only 0.00105693%% of AI-cited content according to an analysis of 94,614 URLs, indicating negligible real-world impact on visibility today.
Only 1 out of 120 top performing companies in AI search published an LLMS.txt file.
Major AI platforms have not committed to parsing LLMs.txt, and Google publicly stated their systems don't currently use it. leaving the file without vendor endorsement.
Developer documentation sites see the most practical value, particularly when serving IDE agents, RAG systems, and coding assistants that actively ingest structured content.
Implementation cost is minimal via auto-generation tools making it reasonable future-proofing for sites with trivial maintenance overhead.
The ecosystem may evolve toward per-page AI signals rather than site-level files, mirroring the progression from site-wide declarations to granular schema markup.
LLMs.txt is a thoughtful proposal that addresses a real need, helping AI systems navigate noisy web content. But it's not a proven route to AI search visibility in 2026. The absence of vendor support, minimal adoption among major brands, and near-zero presence in cited content all point to the same conclusion: LLMs.txt is not yet a meaningful ranking or citation factor.
Do You Need an LLMs.txt to be visible in AI Search in 2026?
Many blogs and social media posts recommend implementing LLMs.txt as a critical step to improve visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT. It would have been easy for me to jump on the hype and sell an LLMs.txt generator or something similar. However, before doing so, I wanted to validate whether it’s actually beneficial.
To evaluate the effectiveness, I conducted a simple study around two central questions:
Does having an LLMs.txt give me an advantage in AI Search?
Assumption: If LLMs.txt provides a measurable advantage, we should see pages with an /llms.txt outperform their peers in AI visibility.
To validate this, I reviewed three different rankings of high performing domains and checked how many of the websites publish an LLMs.txt:
The top 50 of Ahrefs Most cited domains in AI mode
The top 50 of GPT Insights most emotionally powerful German brands in ChatGPT
Using the top 20 domains based on our own AI Search Report: News & Media
The latter two were included to reduce bias and gain different perspectives. Global, high authority domains may benefit from factors beyond LLMs.txt (brand strength, legacy authority, and large SEO budgets). Narrowing the lens to local rankings and a specific industry dataset helps create a more balanced view of this complex topic.
Do AI models use LLMs.txt when retrieving information?
Assumption: If LLMs.txt were a preferred retrieval format, we would see pages with an /llms.txt show up frequently in cited sources used for grounding.
To test this, I pulled a proprietary AI search dataset containing 94,000+ cited URLs from 11,000+ AI responses monitored by ALLMO.ai between August and December 2025. The dataset includes responses from five leading models: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and Perplexity. Responses with no URL citations were removed beforehand. To ensure broad coverage, the prompt set spans multiple industries and intents (B2B, consumer, enterprise, SMB, etc.) and is large enough in scale to support statistically significant conclusions.
But before we dive into the data, let’s quickly clarify what an LLMs.txt is and what it is not.
What LLMs.txt is, and what it is not?
LLMs.txt is a plain text or Markdown file placed at your site's root directory (yourdomain.com/llms.txt) that curates your most important pages and information for AI consumption. Proposed by Answer.AI in September 2024, it's designed to provide large language models with a clean, prioritized map of your content, think of it as a "context guide" rather than an access control mechanism.
Although LLMs.txt is inspired by robots.txt, which was designed for search crawlers and other automated bots, LLMs.txt is not a permission file and not an indexing directive. It does not control what AI systems are allowed to access. Instead, it acts as an AI specific suggestion file, a voluntary signal that highlights which content you consider important for large language models to prioritize when they interact with your site.
The critical distinction is that LLMs.txt remains non-standard. No formal standards body governs its syntax or semantics, and multiple variants exist (per-page Markdown files, llms-full.txt, script embeds). This fragmentation limits consistent parser behavior across AI platforms.
The data: LLMs.txt adoption across dominant players in AI search

Finding: The data shows only 1 out of the 50 most cited domains in AI search has an /llms.txt file. Target.com was the only company with the file available at target.com/llms.txt.
Remarkably Walmart, already had an /llms.txt page publicly available in November 2025, but a follow-up check in January 2026 it in had been removed.
The implication from the first data set is clear: To make it to the top, you don't need an LLMs.txt. fact, there is no indication that it provides a measurable advantage at all, based on the reviewed dataset (see below).
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|
1 | Not found | |
2 | Not found | |
3 | Not found | |
4 | Not found | |
5 | Not found | |
6 | Not found | |
7 | Not found | |
8 | Not found | |
9 | Not found | |
10 | Not found | |
11 | Not found | |
12 | Not found | |
13 | Not found | |
14 | Not found | |
15 | Not found | |
16 | Not found | |
17 | Not found | |
18 | Not found | |
19 | Not found | |
20 | Not found | |
21 | Not found | |
22 | Not found | |
23 | Not found | |
24 | Not found | |
25 | Not found | |
26 | available | |
27 | Not found | |
28 | Not found | |
29 | the‑sun.com | Not found |
30 | Not found | |
31 | Not found | |
32 | Not found | |
33 | Not found | |
34 | Not found | |
35 | Not found | |
36 | Not found | |
37 | Not found | |
38 | merriam‑webster.com | Not found |
39 | Not found | |
40 | Not found | |
41 | Not found | |
42 | Not found | |
43 | Not found | |
44 | Not found | |
45 | Not found | |
46 | Not found | |
47 | Not found | |
48 | Not found | |
49 | Not found | |
50 | Not found |
Next, I reviewed a dataset of the most emotionally resonant German brands in AI Search (GPTInsights). Compared to the Ahrefs dataset above, this ranking differs in three important ways:
Germany-only scope: The dataset focuses exclusively on German companies. While the Ahrefs list suggests you do not need LLMs.txt to be globally dominant, it is still possible that the file could benefit local or niche players.
Mentions, not citations: The dataset tracks mentions rather than grounded citations. This matters because even if LLMs.txt is not used for grounding, it could theoretically influence whether a company is mentioned more frequently.
Resonance-based ranking: The ranking is based on emotional resonance and sentiment, not just citations. In other words, it measures not only whether brands appear in responses, but whether models reflect positive sentiment toward them.
Finding: The results strongly reinforce the Ahrefs conclusion. None of the Top 50 German brands publish an LLMs.txt file.
You can build strong brand positioning that resonates in ChatGPT without LLMs.txt. Again, there is no evidence that such pages provides a measurable advantage for AI Search visibility.
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Marke | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Feuerwehr Deutschland | Not found | |
2 | Ärzte ohne Grenzen | Not found | |
3 | Miniatur Wunderland Hamburg | Not found | |
4 | Landliebe | Not found | |
4 | Milka | Not found | |
6 | dm Drogeriemarkt | Not found | |
6 | Europa‑Park | Not found | |
6 | Ravensburger | Not found | |
6 | Rotes Kreuz (DRK) | Not found | |
6 | Wikipedia (DE) | Not found | |
11 | Haribo | Not found | |
11 | Lidl | Not found | |
11 | Stiftung Warentest | Not found | |
14 | ADAC | Not found | |
14 | Ritter Sport | Not found | |
14 | Schleich | Not found | |
14 | Wacken Open Air | Not found | |
18 | Porsche | Not found | |
18 | WWF Deutschland | Not found | |
20 | Ahoj‑Brause | Not found | |
20 | Bärenmarke | Not found | |
20 | Caritas Deutschland | Not found | |
23 | Duden (Online) | Not found | |
23 | Fressnapf | Not found | |
23 | Glashütte Original | Not found | |
26 | Apotheken Umschau | Not found | |
26 | Not found | ||
26 | Decathlon | Not found | |
26 | Dr. Oetker | Not found | |
26 | Gerolsteiner | Not found | |
26 | NABU | Not found | |
26 | Nutella | Not found | |
26 | Phantasialand | Not found | |
26 | Tagesschau | Not found | |
26 | Vaude | Not found | |
36 | Alnatura | Not found | |
36 | Brot für die Welt | Not found | |
36 | Deuter | Not found | |
36 | Hilton Hotels | Not found | |
36 | Rotkäppchen Sekt | Not found | |
36 | Tempo | Not found | |
36 | Zalando | Not found | |
43 | Amazon | Not found | |
43 | Bosch | Not found | |
43 | Check24 | Not found | |
43 | Coca‑Cola | Not found | |
43 | Ferrero | Not found | |
43 | Faber‑Castell | Not found | |
43 | Fritz‑Kola | Not found | |
43 | Greenpeace Deutschland | Not found |
Last, I analysed data from the ALLMO AI Search Report: News & Media where I regularly share insights on how AI Searches the web. It tracks results across ChatGPT-4, ChatGPT-5 and Perplexity.
This time, we are looking at a dataset from a specific industry. Media companies where reach is critical, and where some players have training data deals with AI Companies.
By zooming in on a specific industry, we can compare apples to apples and test a simple hypothesis: if /llms.txt has a meaningful impact, publishers using it should outperform their peers.
Again, none of the top domains contained an llms.txt, despite being consistently cited as prominent sources over multiple months.
0 out of the Top 20 media and publishing companies have an LLMs.txt
Even platforms like YouTube, which show especially high visibility in Perplexity, do not publish an LLMs.txt.
Notably, even TechCrunch (ranked #1 in the report category “Start-ups & Technology”) has no LLMs.txt. Meanwhile, a little hope for LLMs.txt advocates, TechStartups does implement the standard, ranks #4 in that category, and sits outside the Top 50 overall. In other words: the standard isn’t even widely adopted among tech-forward publishers, and we don’t see an observable performance advantage in this dataset.
Data is as of 21. January 2026.
Rank | Domain | /llms.txt status |
|---|---|---|
1 | Not found | |
2 | Not found | |
3 | Not found | |
4 | Not found | |
5 | Not found | |
6 | Not found | |
7 | Not found | |
8 | Not found | |
9 | Not found | |
10 | Not found | |
11 | Not found | |
12 | Not found | |
13 | Not found | |
14 | Not found | |
15 | Not found | |
16 | Not found | |
17 | Not found | |
18 | Not found | |
19 | Not found | |
20 | Not found | |
21 | Not found | |
22 | Not found |
Lastly, I wanted to evaluate whether llms.txt is a preferred format for AI models when retrieving information via live web search. If the format had a meaningful positive impact, you’d expect many /llms.txt URLs to show up in citations used for grounding, right?
To test this, I downloaded a dataset from the ALLMO.ai database that I had previously used for research and hypothesis testing. It spans a wide range of industries, query types, and research intents, and statistical significance is strengthened by the sheer amount of results as well.
The results were underwhelming.
1 out of 94,614 cited URLs from 11,867 AI responses collected by allmo.ai was an /llms.txt page.
I had hoped to be able to write a longer section with nuanced findings by industry, model differences, or recommendations on which llms.txt structure performs best. But with only 0.00105693% of AI-cited URLs pointing to llms.txt pages, the conclusion stays the same no matter how you slice it.
Across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini, and Grok, there is no indication that models prefer llms.txt pages when performing live web search, regardless of industry, site structure, or llms.txt structure.
More independent evidence
The data paints a sobering picture. Adoption among major brands remains extremely low and is concentrated primarily in developer documentation and technical tooling sites. Despite the proliferation of WordPress plugins and CMS generators that make implementation trivial, fewer than 10% of websites have implemented LLMs.txt according to seranking.com.
But maybe these 10% of companies are the one's that are going through the roof in AI Search? Our data tells a different story.
More critically, major AI and search vendors have not committed to parsing or relying on LLMs.txt. Google Search representatives have publicly stated that their AI systems do not currently use the file. Ahrefs' independent audit found no confirmed visibility uplift attributable to LLMs.txt across major domains.
Consistent with my findings from the ALLMO.ai llms.txt study, SE Ranking's analysis of 300,000 domains reinforced this finding: websites with LLMs.txt showed no statistically significant difference in AI citation frequency compared to those without it.
Limitations
As always, there are limitations to this analysis:
I did not benchmark websites with llms.txt against website without llms.txt
However, if ~10% of websites have adopted LLMs.txt as reported by seranking, you would expect roughly ~10% of cited sources to include it, and even more if it had a positive impact. Instead, I found the file in less than 1% of the 120 analyzed websites. Since the sample spans multiple locations and industries, this effect appears negligible.
I did not evaluate a single websites performance before and after introducing an llms.txt
Everyone is free to test it on their own sites, but such experiments have limited interpretability: AI search algorithms change frequently, making it difficult to isolate the effect of a single change. If there were a consistent preference or measurable uplift, it should have shown up in the citation data. That said, this does not fully rule out edge cases in specific industries or individual setups.
Key Findings: LLMs.txt does not give any quantifiable benefits.
To summarize, here are the results from our extensive analysis of LLMs.txt adoption and citation impact:
1 out of 94,614 cited URLs from 11,867 AI responses collected by ALLMO.ai cited any /llms.txt page.
Only 1 out of 50 most cited domains in AI Search according to Ahrefs use llms.txt
None of the Top 50 strongest emotional German Brands in ChatGPT use llms.txt
None of the Top 20 most cited media and publisher domains use llms.txt.
Neither ChatGPT nor any other analyzed AI model showed a preference for citing LLMs.txt pages, nor did companies with LLMs.txt consistently outrank competitors without it.
Qualitatively, these findings also align with official statements from major AI and search vendors, suggesting there is no hidden preference or roadmap dependency on LLMs.txt today.
This also let's us answer the initial research questions:
Does LLMs.txt give me an advantage in AI Search?
No measurable advantage is visible in current citation patterns.Do AI models use LLMs.txt when searching for information?
We do not see models using it either as a prioritized content map (to cite pages from it), nor as a direct retrieval source during live web search.
So, do you need to add an llms.txt to your website? A decision lens for 2026
The answer depends entirely on what you publish and who consumes it.
You do not need an LLMs.txt if you operate a consumer content site, marketing property, or general publishing platform. There is no proven citation lift for these use cases today, and most visible brands achieve strong AI visibility without it. The data strongly suggests that AI models do not rely on LLMs.txt as a directive mechanism.
That said, there are a few scenarios where publishing an LLMs.txt can still make sense, even though these benefits are not primarily related to AI search visibility.
You should implement LLMs.txt if you run developer documentation, API references, SDKs, or other agent-facing content. These environments can benefit immediately because coding assistants, IDE integrations, MCPs, and RAG pipelines actively seek clean, structured documentation. Providing LLMs.txt and llms-full.txt reduces noise, improves retrieval accuracy, and makes your content easier to ingest programmatically. Cloudflare, Mintlify, and Anthropic publish these files for their developer docs as part of a broader AI-consumability strategy.
The downside of implementing it is minimal when well curated. If your CMS can auto-generate the file, treating it as future proofing can make sense, as long as you do not expect immediate ROI.
Outlook: from one file to per-page AI signals
The LLMs.txt ecosystem may evolve significantly before it matures, or it may fade entirely.
The likely evolution path currently points toward per-page, machine-readable context rather than a single site-level file. Platforms like Context7 are already experimenting with per-page AI metadata that provides granular, document-level signals. This approach mirrors how structured data evolved: from site-wide declarations to page-specific schema markup.
The pragmatic stance for 2026 and beyond: invest in AI-consumable content and reliable agent access now. Treat LLMs.txt as optional scaffolding, not a primary visibility lever. The fundamentals, clear structure, accurate information, machine-friendly formatting, will outlast any single file format.
FAQ: Quick answers about LLMs.txt and AI search visibility
Will LLMs.txt boost my AI citations today?
Unlikely for most sites. Major AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI experiences do not currently appear to rely on LLMs.txt as a primary retrieval or ranking input (based on public statements and independent audits). In addition, ALLMO.ai’s analysis of 94,000+ cited URLs found no measurable citation uplift associated with LLMs.txt adoption.
Is there any harm in adding it?
Usually not, if it’s accurate and maintained. Implementation cost is low, and many CMS platforms offer one click generation.
The risk comes from:
poorly curated files (noise, outdated or incorrect context)
manual effort with low ROI (opportunity cost)
technical SEO mistakes (for example duplicate content or wrong indexing signals if configured incorrectly)
Who benefits most right now from llms.txt?
Developer documentation and API publishers. If your audience uses IDE agents, coding assistants, or RAG pipelines, llms-full.txt and clean Markdown exports can improve machine ingestion because these systems actively seek structured documentation.
My logs shows ChatGPT crawled my llms.txt. So it's useful, right?
Not necessarily. Crawling alone does not imply impact. Bots crawl many pages on most websites, and llms.txt can be treated like any other URL. What matters is whether it shows up in retrieval and citation behaviour, which currently appears rare.
What can I do instead to grow my presence in AI search results
There are many proven ways to improve AI Search visibility beyond LLMs.txt, and the GEO and ALLMO industry is evolving fast, with new tactics and findings emerging constantly. If you want to learn about about ways to optimize your site, talk to me or explore more ways to optimize in The ALLMO Blog.
Key Takeaways
LLMs.txt appears in only 0.00105693%% of AI-cited content according to an analysis of 94,614 URLs, indicating negligible real-world impact on visibility today.
Only 1 out of 120 top performing companies in AI search published an LLMS.txt file.
Major AI platforms have not committed to parsing LLMs.txt, and Google publicly stated their systems don't currently use it. leaving the file without vendor endorsement.
Developer documentation sites see the most practical value, particularly when serving IDE agents, RAG systems, and coding assistants that actively ingest structured content.
Implementation cost is minimal via auto-generation tools making it reasonable future-proofing for sites with trivial maintenance overhead.
The ecosystem may evolve toward per-page AI signals rather than site-level files, mirroring the progression from site-wide declarations to granular schema markup.
LLMs.txt is a thoughtful proposal that addresses a real need, helping AI systems navigate noisy web content. But it's not a proven route to AI search visibility in 2026. The absence of vendor support, minimal adoption among major brands, and near-zero presence in cited content all point to the same conclusion: LLMs.txt is not yet a meaningful ranking or citation factor.
Check out more articles
Start your AI Search Optimization journey today!
Applied Large Language Model Optimization (ALLMO), also known as GEO/AEO is gaining strong momentum.

